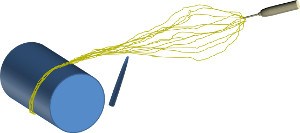
In a standard electrospinning setup, the electrospinning jet spreads out as it moves away from the tip of the spinneret. To induce the jet to converge to a single point and to encourage self-bundling, a grounded needle tip may be used. Conductivity of the solution has been shown to influence the stability of self-bundling and yarn forming. If the solution conductivity is insufficient, self-bundling will cease and the yarn will be discontinuous. It is hypothesized that with sufficient conductivity, electrical charges will discharge from the segment of the jet that is closest to the needle upon contact with it [Wang et al 2008]. This electrically neutral portion of the jet will attract further section which still carries charges. Subsequent collision between these segments of the jet results in bundling behavior and yarn that can be taken up by a roller. In a separate experiment using acrylic terpoymer, it was observed that the resultant yarn did not contain any zigzagging fibers which suggest that the yarn is made out of multiple fibers instead of a single filament that turns back and forth [Mondal et al 2008]. The multiple fibers may be formed by splitting of the primary jet into several jets that converged towards a rod or tip at the time of initiation.
▼ Reference
-
Mondal A, Borah R, Mukherjee A, Basu S, Jassal M, Agrawal A K (2008) Electrospun Self-Assembled Nanofiber Yarns. J Appl Polym Sci 110 pp. 603-607
-
Wang X, Zhang K, Zhu M, Yu H, Zhou Z, Chen Y, Hsiao B S (2008) Continuous polymer nanofiber yarns prepared by self-bundling electrospinning method. Polymer 49 pp. 2755.
Open Access
▲ Close list
 ElectrospinTech
ElectrospinTech